App Cloner comes with the storage option Accessible data directory, which allows you to access the internal files of cloned apps without requiring your device to be rooted. This can be useful for inspecting or modifying internal app data.
To make the internal app files accessible, the cloned app must be started at least once.
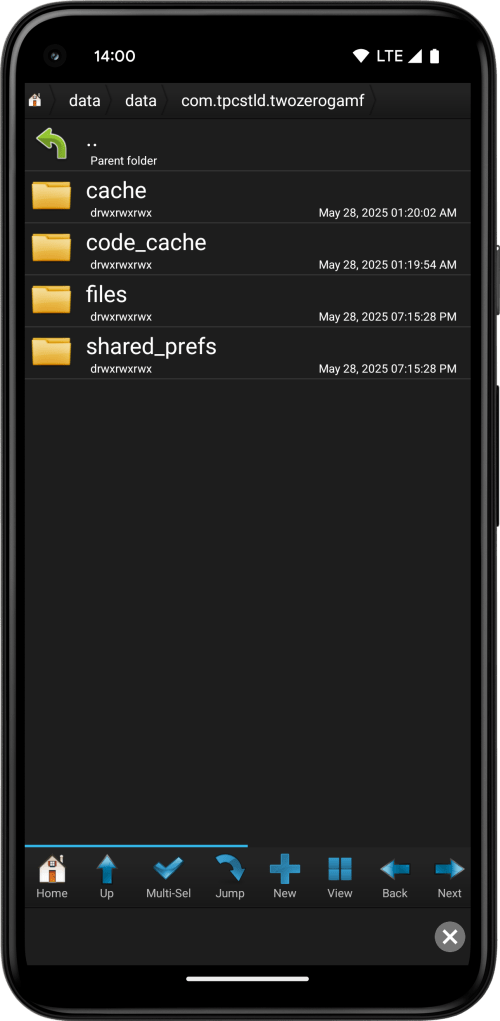
The recommended file browser app for accessing these files is Root Browser Classic (see Android 12+ notice below), which makes it easy to browse and open directories under /data/data/<package-name>, where <package-name> is the package name of the cloned app.
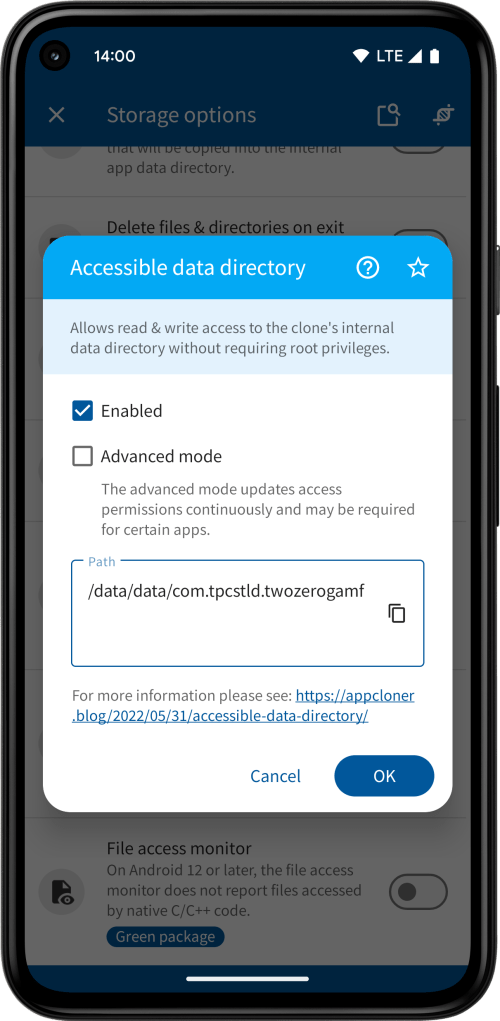
You can enable the Advanced mode to continuously update access permissions while the cloned app is active, even when the app is in the background. This can benefit apps that occasionally reset their file permissions. However, use it only when necessary, as it may affect app performance depending on the number of internal files.
IMPORTANT: On Android 12+ you need to use App Cloner to make a clone of the Root Browser app itself, otherwise it’s not be possible to browse the /data/data directory. It may be necessary to launch the cloned Root Browser app twice after the initial app installation for the cloned app to open correctly. You will also be asked to allow access to manage all files.
On Android 11 and below, if you have a PC with USB or Wi-Fi debugging, you may also access the cloned app’s internal app data directory using adb shell followed by cd /data/data/<package-name>, where <package-name> is the package name of the cloned app.
The complete path can be viewed and copied from the read-only Path text box. Keep in mind that the package name and path varies based on the chosen clone number.
If you prefer to access a cloned app’s internal files via the network, you also have the App Cloner networking option Data directory FTP server.
Finally, App Cloner includes the Documents provider option that makes the app’s internal files accessible through Android’s document provider system.

You must be logged in to post a comment.